新鮮胚胎 VS 冷凍胚胎哪個好

胚胎植入是試管嬰兒療程中的最後一步、也是最重要的,受精成功的胚胎植入進子宮安全抵達堡壘,而且在不需要需麻藥的狀況下就可以進行。
而對於求子的父母親來說,看似簡單的一步卻意義非凡,它是球賽中的臨門一腳,能不能得分獲勝,這一腳是非常重要的。
在國際醫療上植入胚胎的方式有新鮮植入和冷凍植入兩種方式,這兩種的差異性很大,也受用在不同的求子父母親身上。
新鮮胚胎植入
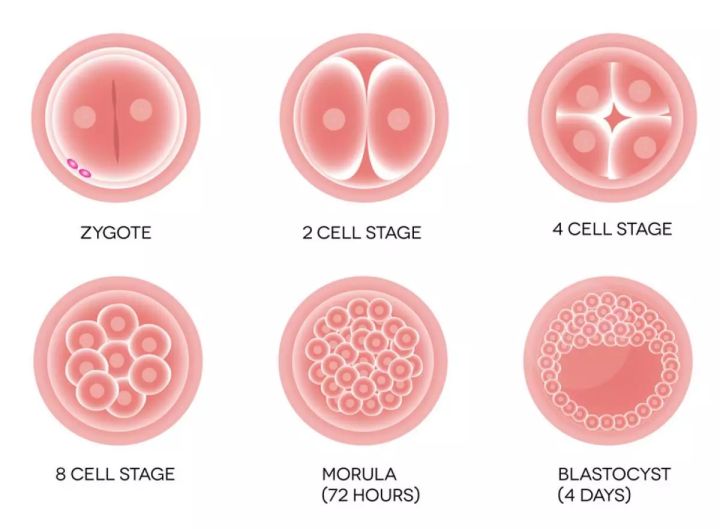
卵子和精子結合後形成受精卵,不斷進行細胞分裂,稱為卵裂(cleavage)。卵裂產生的細胞稱卵裂球(blastomere)。隨著卵裂球數目的增加,細胞逐漸變小,到第3天時形成一個8個卵裂球組成的胚胎。
在試管嬰兒的操作中,會將這個在第3天形成的胚胎簡稱為早期胚胎,目前採用的植入方式為新鮮胚胎植入。
而囊胚則是指,胚胎繼續長,到了第四天形成一12~16個卵裂球組成的實心胚,稱桑椹胚(morula)。桑椹胚的細胞繼續分裂,細胞間逐漸出現小的腔隙,大約兩天後他們最後匯合成一個大腔,桑椹胚轉變為中空的胚泡。胚泡也就是我們所知道的囊胚(blastocyst),這個時候是受精卵的第5天。此時為新鮮囊胚植入。
優點:縮短整體試管嬰兒治療時間(如果可以成功的話)。對於那些對懷孕渴望已久的求子夫妻來說,新鮮囊胚移植會在取卵後不久進行,可以有效縮短時間,如果成功,那意味著您可以更快擁有自己的寶貝。
缺點:由於促排卵藥物會導致血中荷爾蒙濃度上升,在進行新鮮囊胚植入時,過高的荷爾蒙也時會給植入帶來一些麻煩,如卵巢過度刺激症候群(OHSS)。另外,過高的黃體激素也會讓子宮內膜提早黃體化或是老化,使得子宮內膜環境對於胚胎的接受度降低,導致胚胎難以著床。
冷凍胚胎植入
將胚胎和冷凍液裝入冷凍管中,經過降溫使胚胎靜止下來,然後再在-196度的液氮中保存。一般凍胚是在同時培育出多個胚胎的情況下,保證鮮胚的植入後,將剩餘的品質較好的胚胎冷凍保存,待以後自然週期或人工週期解凍後植入子宮腔內,以增加受孕的機會。
優點:避免或降低遲發性卵巢過度刺激症候群(OHSS)。在取卵和新鮮週期植入的過程中,會有較高的卵巢過度刺激症候群發病幾率。在卵巢經過荷爾蒙刺激之後,多餘的人體絨毛膜促性腺激素(hCG)會誘發產生遲發性卵巢過度刺激綜合症(OHSS)。儘管情況通常較輕微,但OHSS會引發黃體囊腫(corpus luteum)產生大量激素,如:雌激素,黃體素和細胞激素。多數情況下,腫脹和激素濃度的增加都在可接受範圍之內,但部分少見的極端情況可能會對孕婦及胎兒產生一些危險。而凍胚移植則可以有效的減少或避免這種情況的發生;另外,解凍植入時,由於沒有取卵時所產生的的高濃度荷爾蒙,因此子宮內膜比較不會提早黃體化,對凍胚的接受度更高。
患者的子宮可以在準備凍胚植入的過程中得到更好的修養和復原,從而能夠在接受移植時達到更好的狀態;有一些研究甚至認為通過冷凍囊胚出生的胎兒可能會更加健康,極少數會出現出生體重輕或個頭較小的問題。
缺點:相比新鮮囊胚移植,冷凍胚胎植入需要更長的等待時間才可最終懷孕。此外,冷凍胚胎植入等待時間對於一個渴望嬰兒的家庭來說都是漫長的。而再多等待一個月來進行凍胚移植,似乎會更為煎熬。
什麼人適合新鮮胚胎植入?
•取卵數量不會過多 ( 如 10 顆以下 ),避免卵巢過度刺激症候群
•打破卵針當天雌激素不會太高,最好<2500 pg/ml
•打破卵針當天黃體素不會太高,最好<1.0 ng/ml
•內膜厚度適當 8~15 MM 左右
•無特殊發炎或是出血狀況
什麼人適合冷凍胚胎植入?
•取卵數量多(例如15顆以上),有高風險卵巢過度刺激症候群
•打破卵針當天雌激素太高,>3000 pg/ml
•打破卵針當天黃體素太高,>1.5 ng/ml
•內膜厚度不適當,小於7MM或是大於15MM
•當週期促排卵藥物使用高劑量藥物
•骨盆發炎感染或是有出血狀況
•過去曾有著床失敗的狀況
•懷疑有免疫反應過度干擾胚胎著床,應先處理再植入
•子宮內膜異位症或是嚴重子宮肌腺症,需藥物治療才能安排植入
•有作植入前胚胎切片檢查,PGS或PGD的需求
鍾繼賢醫師:以綜合評估來說植入解凍後的高品質囊胚的成功率可能較為最理想的。但是在現實生活中因為實際情況不同,所以需要根據自身的情況來採取植入措施,另外聽醫生的意見才能早日懷上自己的寶寶。

